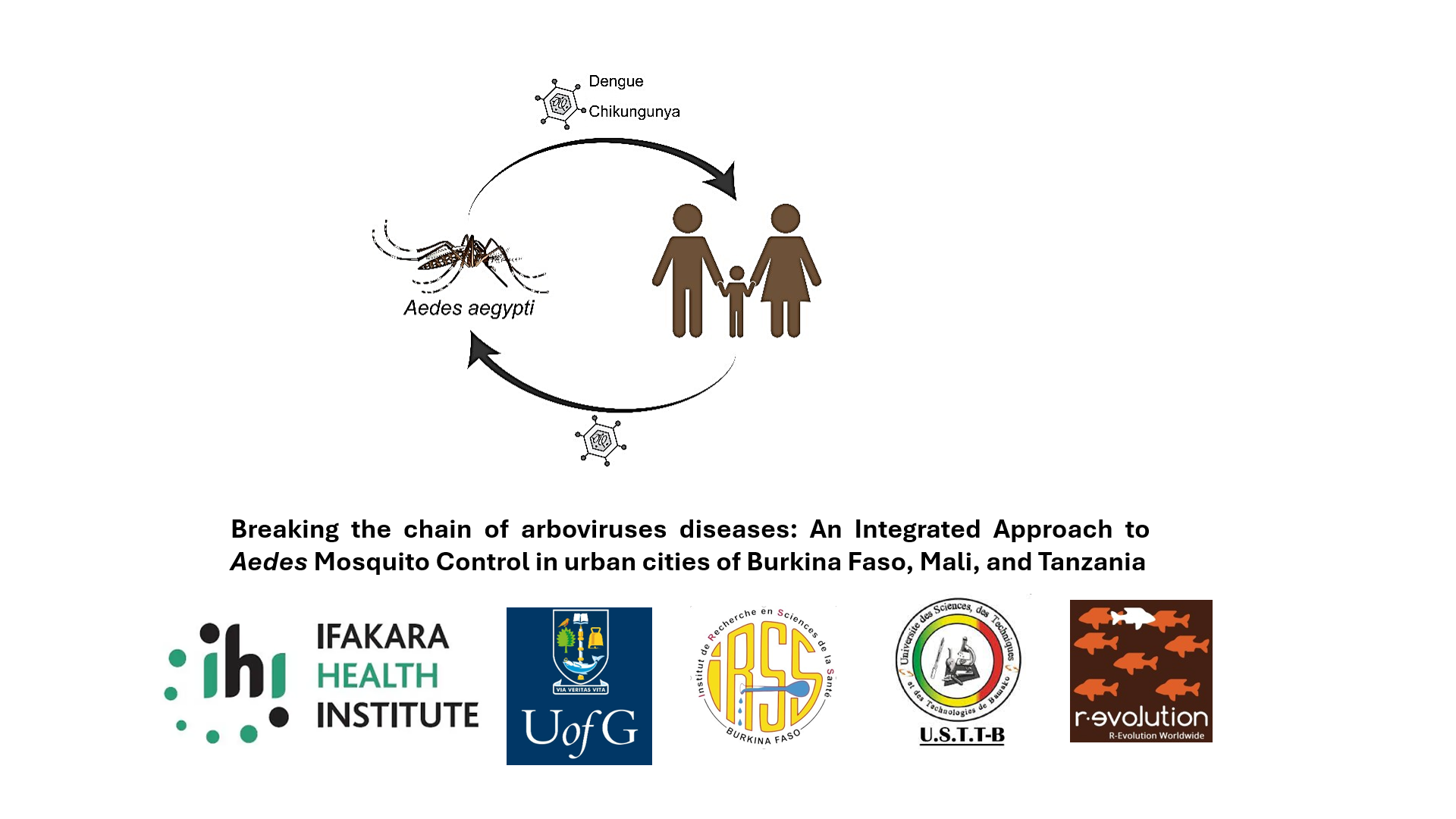
The increasing urbanization in Africa, paralleled by inadequate environmental sanitation, significantly contributes to the proliferation of Aedes mosquitoes, which transmit many arboviruses, including dengue virus (DENV) and Chikungunya virus (CHIKV).
In 2023, a total of 70 223 cases of dengue and 753 deaths have been reported from 15 African countries. Burkina Faso continues to be the country most impacted, accounting for 85% of reported cases and 91% of recorded fatalities. In 2023 Mali experienced simultaneous outbreaks of dengue and chikungunya infections.
The VectorEnd project promotes an integrated vector control approach to mitigate the burden of dengue and chikungunya, in urban areas of Burkina Faso, Mali, and Tanzania with high incidences of these diseases.
This initiative marks the first comprehensive trial in African urban settings to assess the combined effect of mass trapping, larval source management, and community engagement on controlling Aedes mosquitoes and the diseases they transmit.