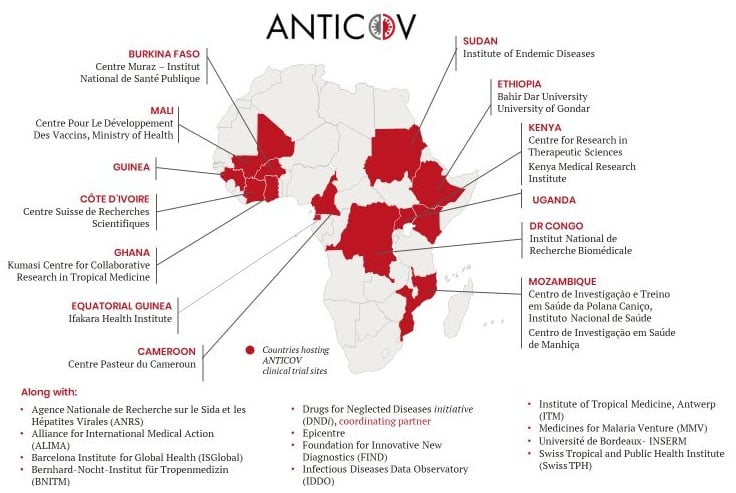
A multidisciplinary consortium of African and European researchers responded to the urgent call from the European Union by developing a research project on the current Monkeypox outbreak in central Africa.
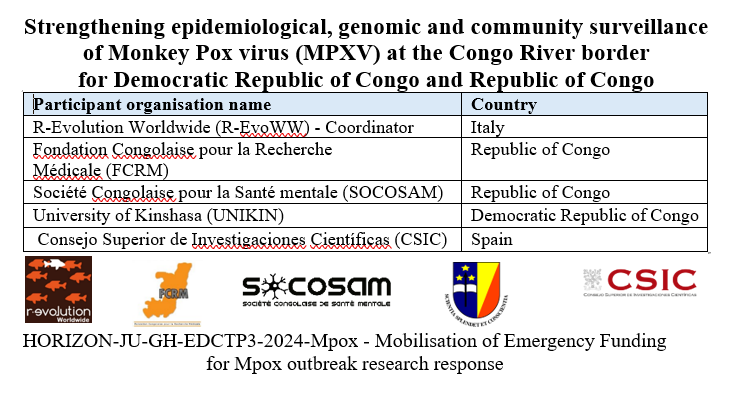
The spread of Mpox virus (MPXV) in Sub-Saharan Africa, specifically Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and Republic of Congo (RoC) presents an urgent public health concern with global implications. MPXV cases