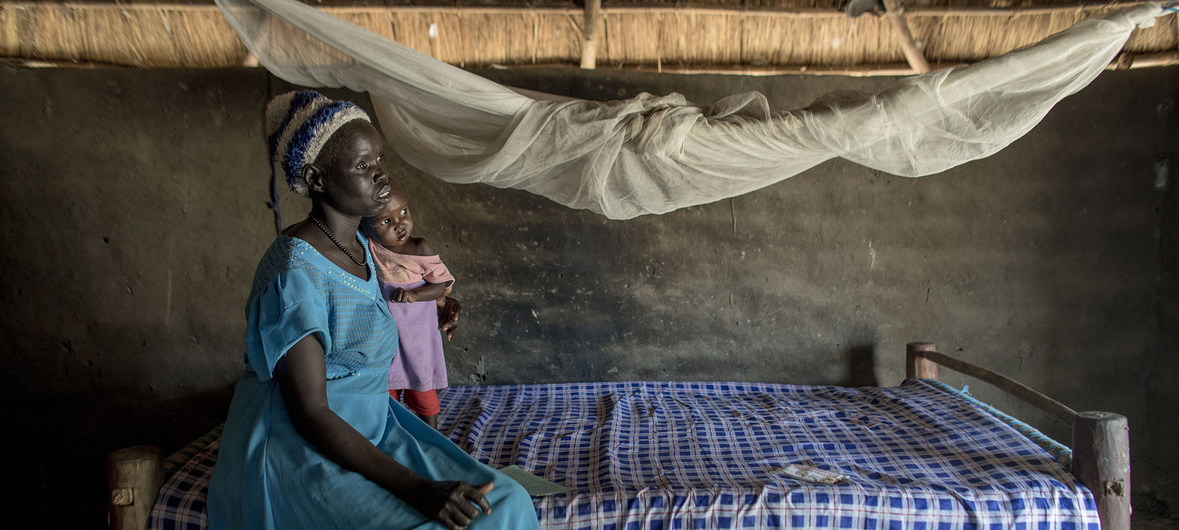
In Africa, pregnant women and young children are the most vulnerable to malaria.
However, malaria control interventions and strategies have achivied important results in the last years.
COVID-19 has now made these interventions critical, and could undo the results obtained so far, as highlighted by scientists in the Lancet: https://bit.ly/2Tfyxwn.
Potentially, COVID-19 could indirectly cause more deaths than it already does directly, in the context of Africa’s weak and fragile health systems.