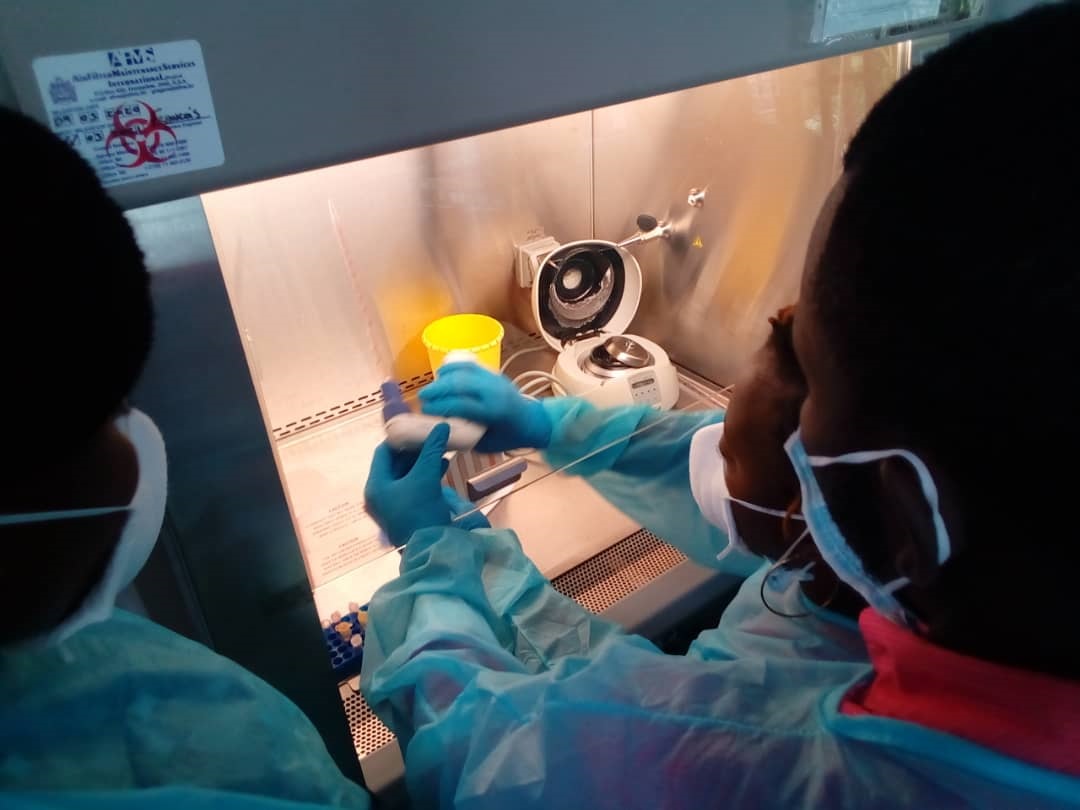
As part of the implementation of ITAIL-COVID-19 project funded by the European Development Countries Partnership for Clinical Trials (EDCTP) and coordinated by the Congolese Foundation for Medical Research (FCRM), the Congolose team of this project participated on January 14, 2021 in the second online practical training on “SARS-CoV-2 detection by the ApoH“. Supervised by the French Research Institute for Development (IRD), this second practical training allowed participants to become familiar with this ultrasensitive virus detection technique. The training on this new technology was carried out by Dr. Carolyn Thibal (ApoH-Technologies) and Professor Francisco Veas, from IRD Montpellier – France. This technique will detect newly infected people with very low viral load, not possible to be detected with conventional methods, including classic RT-PCR. This ApoH detection will be very helpful for monitoring health workers who are at the forefront of the fight against the pandemic. The first training was held on September 2020.